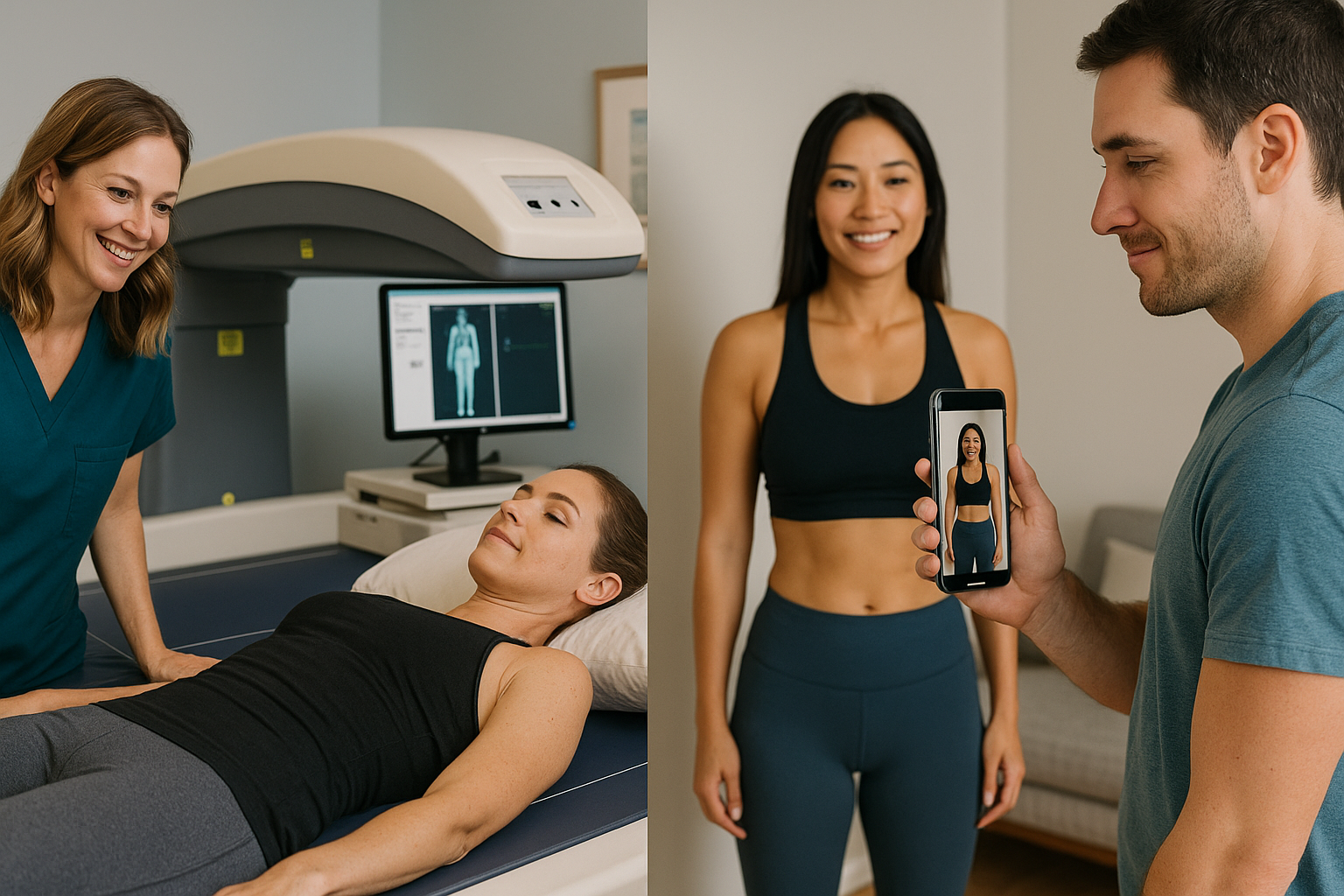
Introduction
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) has long been considered the gold standard for body composition analysis. This comprehensive guide explores how DEXA technology works, its applications, and its role in modern health assessment.
How DEXA Technology Works
DEXA scans use two different X-ray energy levels to distinguish between different tissue types:
- Low-energy X-rays are absorbed by fat
- High-energy X-rays pass through fat but are absorbed by lean tissue
- Bone absorbs both energy levels
- Computer algorithms calculate tissue composition
Clinical Applications
DEXA scans are used in various clinical settings:
- Osteoporosis screening and monitoring
- Body composition assessment
- Fitness and athletic performance evaluation
- Research studies
- Medical weight management programs
Advantages of DEXA
DEXA offers several advantages over other body composition methods:
- High accuracy and precision
- Regional body composition analysis
- Low radiation exposure
- Established clinical validation
- Comprehensive reporting
Limitations and Considerations
Despite its advantages, DEXA has some limitations:
- High cost ($100-300 per scan)
- Limited accessibility
- Requires specialized equipment
- Appointment scheduling required
- Radiation exposure (minimal but present)
Conclusion
DEXA remains the gold standard for body composition analysis in clinical settings. While emerging AI technologies offer increased accessibility, DEXA provides the accuracy and precision required for medical applications and research.