Introduction
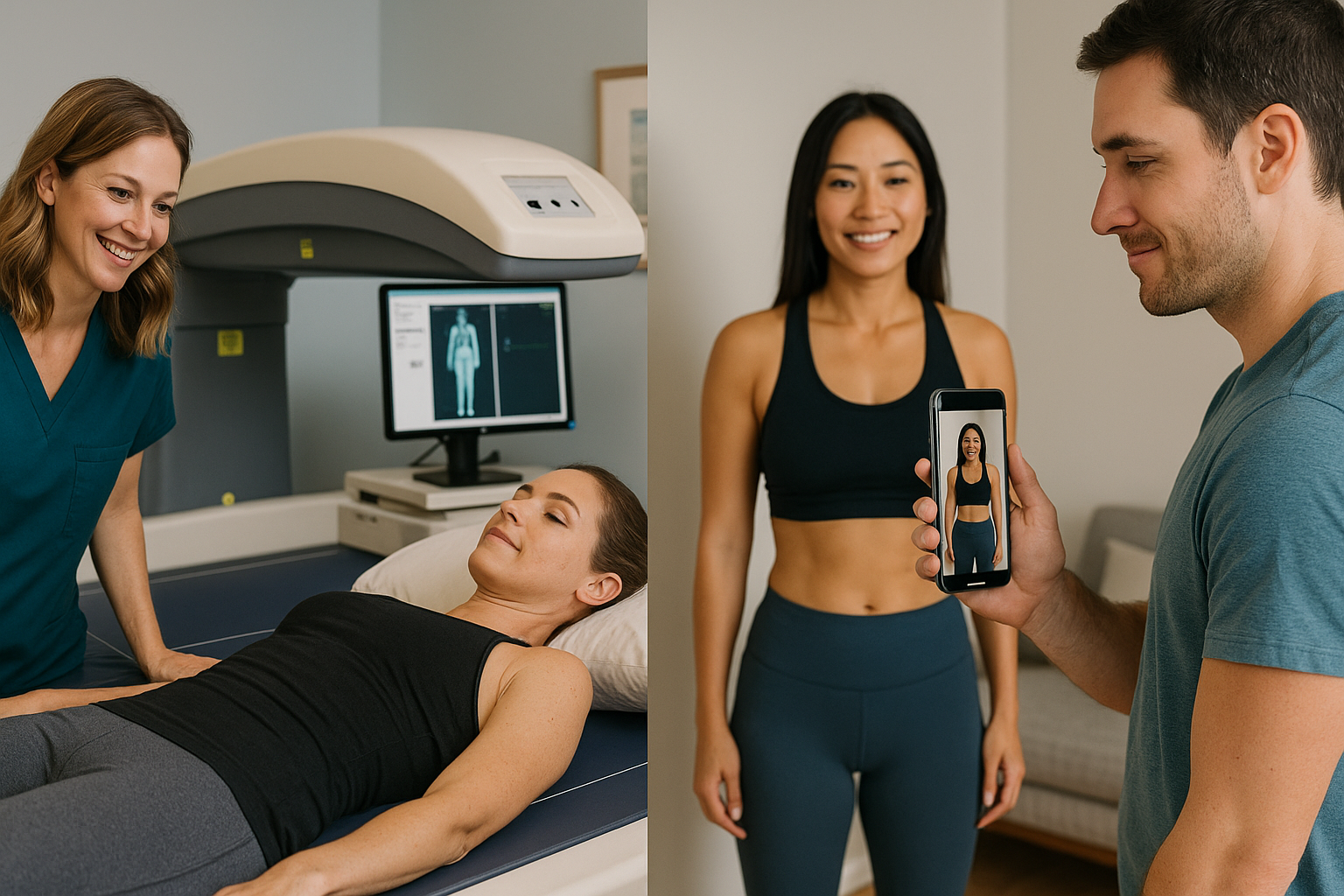
Body composition analysis has evolved significantly over the years, with two main technologies dominating the market: traditional bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) devices like InBody and modern AI-powered body scanning solutions. This comprehensive comparison explores the strengths and limitations of each approach.
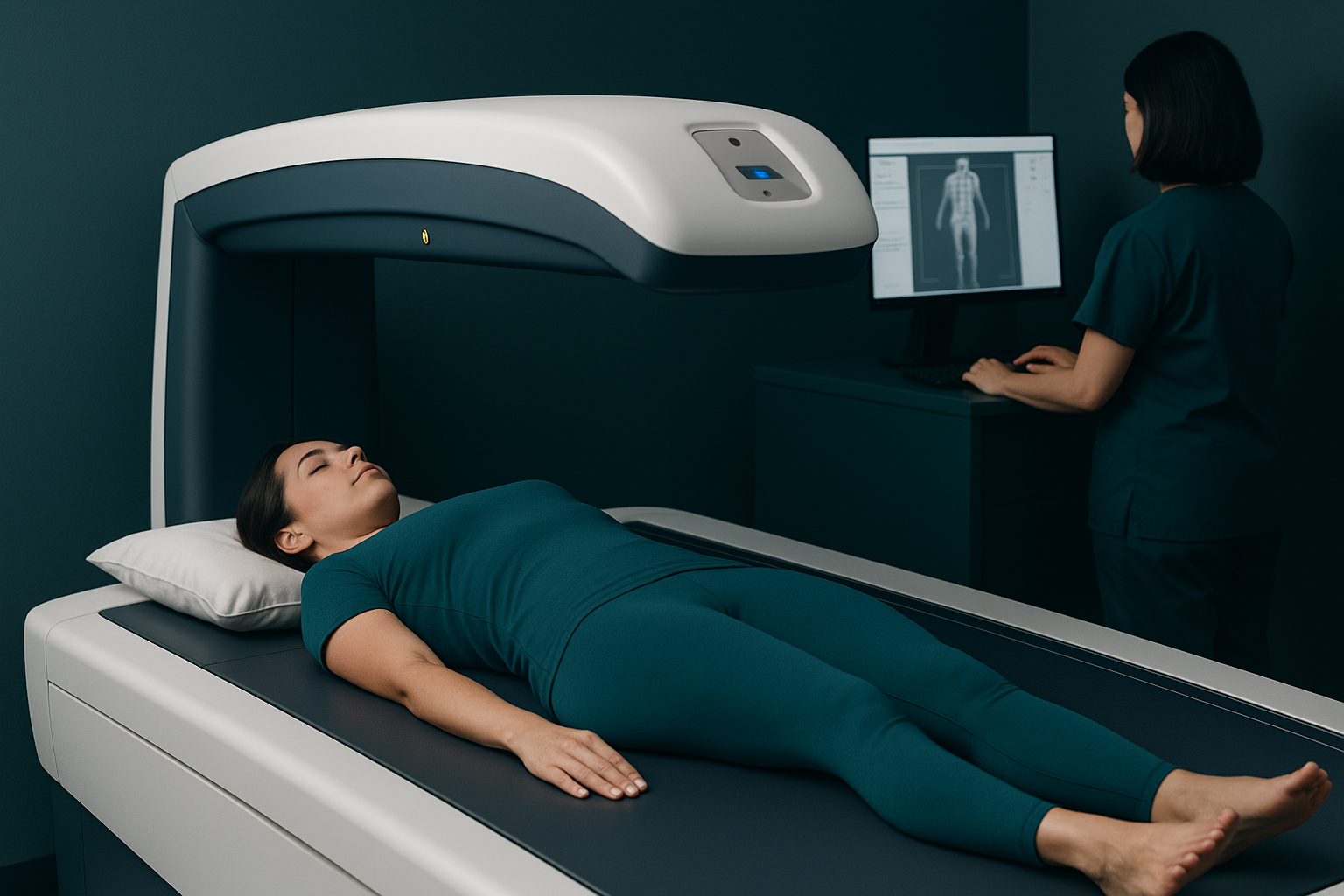
InBody Technology Overview
InBody devices use bioelectrical impedance analysis to measure body composition by sending electrical currents through the body. Key features include:
- Multi-frequency analysis
- Segmental body composition measurement
- Established clinical validation
- Comprehensive body composition reports
- Professional-grade accuracy
AI Body Scanning Technology
AI-powered body scanning uses computer vision and machine learning to analyze body composition from photographs. Key advantages include:
- Non-invasive measurement
- Accessible via smartphone
- No special equipment required
- Immediate results
- Cost-effective solution
Accuracy Comparison
When comparing accuracy between InBody and AI solutions:
- InBody: 95-98% accuracy for body fat percentage
- AI scanning: 90-95% accuracy in optimal conditions
- Both methods affected by hydration status
- AI accuracy depends on image quality and positioning
Practical Considerations
Choosing between InBody and AI depends on several factors:
- Budget constraints
- Accessibility requirements
- Frequency of measurements
- Clinical vs. personal use
- Integration with existing systems
Conclusion
Both InBody and AI technologies offer valuable insights into body composition. InBody remains the choice for clinical settings requiring maximum accuracy, while AI solutions provide accessible, cost-effective monitoring for personal use and frequent tracking.